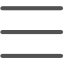
Our ear consists of three main parts; the outer, middle, and inner ear. Sound waves pass from the outer ear toward the inner ear as vibrations. We then convert these vibrations to signals that travel to the brain. This is what allows us to hear, however, hearing is not your ear’s only function. The tiny fluid-filled tubes in the semicircular canals of your inner ear contribute to your sense of balance. So, anything affecting these processes affects both your hearing and balance. Benign and malignant tumour’s, ear inflammation and other ear problems are not uncommon.
Leading Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) surgeons Dr Simon Braham and Dr Stephen Kleid offer various treatments for ear problems and disorders in Melbourne, Australia. Their experience encompasses a wide array of both surgical and non-surgical treatments for diseases involving hearing and the ears.
Continue reading to find out more about the types of ear problems, as well as the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for each.
Range of Ear Concerns and Conditions We Treat
- Ear Ache
- Sudden Hearing Loss
- Hearing Loss in Children
- Tinnitus
- Glue Ear (Adhesive Otitis)
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
- Middle Ear Infection (Acute Otitis Media or AOM)
- Swimmers Ear (Otitis Externa)
- Structural Concerns of the Ear – like Overly Prominent Ears
Ear Ache
Earaches are a common ear complaint rather than an independent condition. It is a result of either an infection or inflammation in any of the three parts of your ear: the outer, middle, or inner ear. Earaches are more common in children than adults and can affect one or both ears.
What Are the Symptoms Associated with Earache?
Although the symptoms depend on the cause of your earache, common symptoms of ear infection and inflammation include:
- Ear pain
- Sore throat
- Vertigo; refers to a spinning feeling
- Tinnitus is the medical term for ringing in the ear
- Fever
- Swelling
- Redness
What Causes Earache?
Infections, irritations, or injuries to your ear are common causes of earache. However, referred pain or pain felt in other areas may also lead to pain in your ear.
Other causes of earache include:
- Middle ear infection
- Trauma
- Temporomandibular joint infection
- Bullous myringitis
- Dermatitis
- Sunburn
- Swimmer’s ear
How Is Earache Evaluated?
An appointment with Dr Kleid involves physical examinations and diagnostic tests for an accurate and expert diagnosis of your problem.

- Otoscopy
- Dr Kleid uses an otoscope, a lighted instrument, to look inside your ear. This allows him to examine your inner ear for redness or other symptoms of infection or disease.
- Hearing test
- Hearing tests evaluate your ability to hear sounds at different pitches.
- Through your hearing test results, Dr Kleid can determine if you are experiencing a hearing loss in one or both ears.
- This can help narrow down the cause of earache.
- Laboratory tests
- Dr Kleid may take a sample from your ear fluid for laboratory testing.
- Lab tests can determine either the cause of your pain or rule out other conditions.
- Imaging test
- He can also request an MRI or CT scan to investigate the cause of your ear pain further.
How Are Earaches Treated?
The treatment options will depend on the specific cause of your earache. In most cases of earaches, your doctor will prescribe either eardrops or antibiotics.
- Eardrops:
- Can be used for treating earache caused by a build-up of wax in your ear canal.
- Eardrops soften and break down the wax so it can be removed.
- Antibiotics:
- Antibiotics may treat infections like otitis media and bullous myringitis that may be causing your earaches.
What Are The Complications Of Earache?
If caused by infections, your earache may resolve without medical intervention. But antibiotics and pain relief methods will make for speedy healing and recovery.
Glue Ear (Adhesive Otitis)
Glue ear, or adhesive otitis, occurs when your middle ear becomes filled with sticky, glue-like fluid. This usually happens after an infection, like a common cold.
When the fluid persists, it becomes sticky and stops the tiny bones in your middle ear from carrying sound vibrations to your cochlea, a hollow, spiral-shaped bone in the inner ear. Furthermore, this lack of vibration can lead to temporary hearing loss.
What Are The Symptoms Of Glue Ear?
Glue ear symptoms are not definite, but glue ear may be noticed when you:

- Speak more loudly or quietly than usual
- Struggle to hear people
- Listening to very loud music or TV
- Easily get distracted when people talk
- Become either tired or irritable when trying to listen
What Causes Glue Ear?
Causes and risk factors of glue ear include:
- Children below 2 years old
- Bottle-feeding
- Seasonal allergies
- Exposure to tobacco smoke
- Recent cold or flu
Anything that leads to the accumulation of fluids in your middle ear can cause glue ear, it is common in children because their ‘eustachian tube’ is narrower than adults.
The eustachian tube is a passage that runs from the nose to the middle ear, it also drains mucous. Some cases, like severe allergies, can lead to a swollen and constricted eustachian tube and then fluid build-up.
How Is Glue Ear Diagnosed?
Dr Kleid diagnoses glue ear with the use of an otoscope (which helps him look inside the ear), it also allows him to check if there are any infections or other ear problems.
How Is Glue Ear Treated?
Most cases resolve independently, but glue ear may need to be treated with antibiotics if it gets infected. Some treatments for glue ear include:
- Speech Therapy And Hearing Aids
- If glue ear remains untreated, it can affect your child’s ability to speak properly.
- Dr Kleid recommends both speech therapy and hearing aids for severe and chronic glue ear cases.
- This can help improve auditory skills whilst also lessening the negative impact it has on your child’s development.
- Surgery
- If glue ear stays long-term, Dr Kleid can treat it with adenoidectomy, wherein he removes your adenoid glands from behind your nose.
- Enlarged adenoids can block the eustachian tube and are a common contributor to the fluid accumulation in the middle ear.
If hearing loss persists, Dr Kleid may insert tiny tubes called grommets into your ear to allow air to drain the fluid.
What Are The Complications Of Glue Ear?
Glue ear can take three months or more to clear up. If it has yet to resolve and is left untreated, glue ear can induce ear infections. A delay in speech and language development in children can also occur when hearing loss is severe.
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
Fluid in the ear or “otitis media with effusion” (OME) means an abnormal accumulation of fluids in the middle ear, behind your eardrum, affecting the function of your eustachian tube. The eustachian tube is a narrow passage connecting your throat to your middle ear.
OME is usually associated with non-infected fluid, however, if it persists, the fluid may become infected. When infection occurs, it is called acute otitis media (acute middle ear infection).
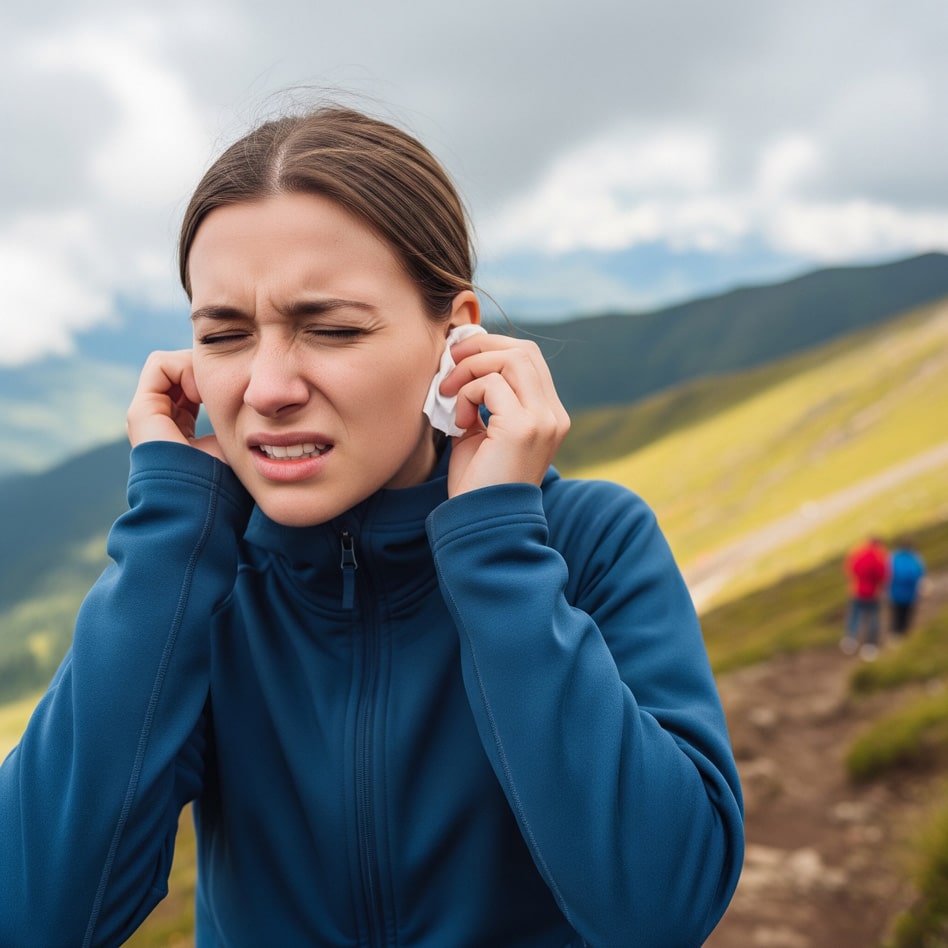

What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Media with Effusion?
Some cases of OME are asymptomatic, in other words, they show no symptoms whatsoever. Symptomatic patients of otitis media with effusion present the following:
- Vertigo, the feeling of spinning
- Tinnitus, ringing in the ear
- The feeling of fullness in the ear
- Hearing loss
- Plugged up ear from high blood pressure
- Earache during altitude change
What Causes Otitis Media with Effusion?
Otitis media with effusion usually stems from a eustachian tube that is functioning poorly. The eustachian tube has a role in balancing the air pressure inside your middle ear, it also has a role in removing fluid and debris. Normal fluid drainage from your middle ear can’t be done when its function is impaired, leading to fluid build-up.
These are some reasons why your eustachian tube might not be functioning right, increasing your risk of OME, including:
- Allergies
- Congestion
- Tissue enlargement
- Exposure to chemicals
- Trauma
- High blood pressure
- Down’s syndrome/cleft palate
- Damage to the auditory tube
How Is Otitis Media with Effusion Diagnosed?
If you notice any of the symptoms, consult an otolaryngologist like Dr Kleid for a proper evaluation of your ear condition.
- Otoscopy:
- Dr Kleid may use a pneumatic otoscope that blows air into your ear to inspect your eardrum’s movement.
- If it doesn’t move freely, this indicates there is fluid accumulation in the middle ear.
- Tympanometry:
- In tympanometry, Dr Kleid uses a speculum.
- He will place it on the outer portion of your ear canal, measuring the air pressure inside.
- This is to test how well your middle ear is working and if there are any significant pressure changes.
How Is Otitis Media with Effusion Treated?
Typically, when you develop fluid in the ears, it resolves within 4 to 6 weeks, and treatment is unnecessary. But if it does not, treatment will depend on the duration of fluid accumulation.
- Antibiotics:
- If your OME accompanies a respiratory infection, Dr Kleid can prescribe antibiotics to treat it.
- Myringotomy:
- Dr Kleid may perform a myringotomy, the surgical placement of ear tubes into your middle ear.
- These ear tubes aid in draining the fluid which also helps relieve the pressure.
- Myringotomy is usually recommended at the 12-week mark of OME.
What Are The Complications Of Fluid In The Ear?
Some cases of OME may lead to more severe issues such as acute otitis media, fluid in the ear with an active infection. Children are at higher risk since they may suffer from developmental delays due to hearing loss. However, permanent hearing loss due to fluid in the ear is very rare if properly treated.
Middle Ear Infection (Acute Otitis Media, AOM)
The medical term for inflammation or infection of your middle ear is acute otitis media (AOM). This is often due to a virus or bacteria infecting your middle ear. AOM is more likely to affect children than adults, but it may resolve independently or with minor treatment.
What Are The Symptoms Of Middle Ear Infection?
The onset of AOM symptoms is usually rapid but may also differ from case to case.
- Discharge of fluid from the ears
- Ear pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Fever
- Hearing difficulties
- Irritability
- Loss of balance
- Difficulty sleeping or staying asleep
What Causes Middle Ear Infections?
Infection of your middle ear may stem from prior respiratory bacterial or viral infection (like a common cold). A sore throat or cold may spread to the middle ear and result in fluid build-up behind the eardrum. All this can lead to congestion or swelling of the lining of the throat, nose, and eustachian tubes.
Other factors that increase the risk of middle ear infection include:
- Malformation of the eustachian tube
- Recent cold
- Allergies
- Upper respiratory problems and infections
How Is Middle Ear Infection Diagnosed?
Since the signs and symptoms of an ear infection can resemble other conditions, Dr Kleid may perform or request other diagnostic tests to diagnose acute otitis media:
- Otoscopy:
- A pneumatic otoscope blows a puff of air into the eardrum to check your eardrum movement.
- If Dr Kleid observes little to no movement of your eardrum, your middle ear is filled with fluid that may be infected.
- Tympanometry:
- Tympanometry makes use of air pressure to check for fluid in your middle ear.
- Dr Kleid uses this to evaluate your eardrum movement.
- Little to no movement means that there is fluid build-up that could be infected.
How Is Middle Ear Infection Treated?
Treatment for a middle ear infection is based on your age, health and medical history, as well as, the severity of the condition:
- Medication:
- Over-the-counter medication and pain relief ear drops are common treatments for reducing the pain of acute otitis media within a few hours.
- Antibiotics:
- Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics if the cause of your otitis media is bacterial.
- Antibiotics are only given if the infection does not clear up on its own.
- Myringotomy With Placement Of Tube:
- We recommend this surgical procedure if you suffer from chronic ear infections.
- Dr Kleid inserts a tiny tube through an incision in your eardrum.
- This tube allows air into your middle ear, effectively draining any fluid.
Myringotomy can take less than 10 minutes, and the tube can stay in place for up to 12 months.
What Are The Complications Of Otitis Media?
If left unchecked middle ear infections can result in permanent hearing loss. This in turn can lead to impaired speech and language development in children. Infections may also spread to other parts of the head (like the brain), causing more significant disorders (e.g. meningitis, encephalitis).
Swimmer’s Ear (Otitis Externa)
Otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, is an infection of the outer ear. The outer ear canal starts from your eardrum and extends to the outside of your ear. Swimmers ear is usually a bacterial infection that is a result of persistent water in the outer ear canal.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Swimmer’s Ear?
Symptoms associated with otitis externa include:

- Ear pain
- Visible redness
- Swelling
- Drainage of clear, odorless fluid
- Itching of the ears
The symptoms usually develop quickly over 1-2 days, and you’ll notice them as they occur.
What Causes Swimmer’s Ear?
Otitis externa is a result of water persistently entering your outer ear canal. This provides a moist environment for bacteria to grow, which in turn leads to infection. The condition is, therefore, commonly encountered in swimmers.
Risk factors that make you more susceptible to swimmer’s ear include:
- Excess moisture in the ear canal, either through heavy perspiration or humid weather
- Exposure to contaminated water with high bacteria levels
- Skin break that facilitates infection, for example, scratches and/or abrasions
How Is Swimmer’s Ear Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of an external ear infection is usually straightforward. You won’t need a lab test, just a physical examination of your ear canal and eardrum with an otoscope. If required, tests and discharge sampling will be carried out to know the primary site of infection and its cause.
How Is Swimmer’s Ear Treated?
Treatment of otitis externa aims to stop the infection and allow your ear canal to heal. It may include:
- Cleaning:
- Dr Kleid may use a suction device to clear out debris, discharge, or earwax that may block eardrops from reaching the target area in your ear.
- Medication:
- Most medications for swimmer’s ear are in the form of eardrops. There are different types of eardrops to treat different types of infection. You can also use over-the-counter pain relievers to ease your discomfort.
What Are The Complications Of Swimmer’s Ear?
If treated early, swimmer’s ear doesn’t have any complications, however, if left untreated, the infection can become widespread, moving to your deep tissues and becoming a long-term infection. The infection can even spread to bones and cartilage, causing osteomyelitis, as well as, bone and cartilage damage.
Common Ear Problems and Disorders FAQs
What are the most common ear problems?
The most common ear problems we encounter in our ENT clinic include;
- Swimmers Ear
- Middle and outer ear infections
- Glue Ear
What are some symptoms of ear disorders?
Symptoms common to ear disorders include;
- Loss of balance
- Vertigo
- Tinnitus
- Swelling
- Pressure in the ear.
It’s usually hard to tell what exact condition is causing the symptoms without proper examination.
Can ear problems affect your brain?
Yes. If left untreated, ear infections can spread to the brain. They can be a cause of meningitis or encephalitis and lead to severe adverse outcomes.
What causes the ears to hurt inside?
Either allergies, colds or sinus infections can affect the anatomy of your ear, which can cause pain. Whereas, ear infection, otitis media, otitis externa, and impacted wax, can all be causes of earache.
What are the symptoms of inner ear damage?
Symptoms of inner ear damage include earache, tinnitus, hearing loss, fullness in your ear, and vertigo.
Can ear problems affect memory?
Cognitive overload may occur in a mild loss of hearing. It may lead to hearing-related memory loss in some people.
Can your ear tumour be cured?
If the tumour is only in the ear canal, yes it is possible to cure it through surgery, especially if diagnosed early.
What happens if hearing loss is not treated?
If you don’t treat hearing loss, it can lead to emotional troubles like depression, stress, tension and fatigue, as well as, withdrawal from social functions. Moreover, it reduces your ability to perform many professional and everyday tasks. In children, untreated hearing loss can lead to speech development problems.
Is tinnitus associated with Alzheimer’s?
Studies have shown that you stand a higher risk of developing either Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s if you have tinnitus.
Sources:
Further Reading
- Read more about Throat Concerns and Conditions
- Read more about Nose Concerns and Conditions
- View Before and After Gallery
Why Choose Dr Kleid ?

Dr Stephen Kleid,
Melbourne ENT Surgeon
MED0001052799
Dr Stephen Kleid is an experienced ENT Surgeon (Otolaryngologist) based in Melbourne with a passion for Septo-rhinoplasty, Septoplasty and a strong interest in Rhinoplasty Revision.
Qualifications
- AHPRA (Medical Board)
- MB, BS; FRACS (Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons)
- AAFPS – Member of the Australasian Academy of Facial Plastic Surgery
- AAFPRS – (International Member of the American Academy of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons)
Dr Kleid’s Procedures
Why Choose Dr Braham ?

Dr Simon Braham,
Melbourne ENT Surgeon
MED0001144757
Dr Simon Braham MBBS (Hons) FRACS is an experienced Ear, Nose and Throat ENT Surgeon (Otolaryngologist) based in Melbourne, performing tonsil, grommet and sinus surgery for children & adults. He helps patients with breathing issues, snoring concerns and sleep disturbances.
Dr Braham’s Procedures
How can we help?
The Melbourne ENT Team takes pleasure in assisting you with any questions when considering a plastic surgery procedure. Please call the St Kilda East clinic in Melbourne between 9am – 5 pm on Weekdays.
What Next?
Want more information about your Procedure?
- Please read our website and blogs to find out more about your procedure and concerns
- For more information about pricing and payment methods, please visit our page on Surgery Payment Options.
- Talk to our Patient Care Team from 9 am to 5 pm Monday to Friday

What to Bring to Your Consultation
- We encourage you to bring a friend or family member to accompany you, as they can provide an extra perspective and support throughout the process.
- It is important to take thorough notes and carefully review all the documents provided to you.

How to Book a Consultation
- A referral from your GP or Specialist is necessary to see a surgeon for a consultation.
- Dr Kleid’s Nose Surgery consultation fee is $600 which includes a nasendoscopy ($300).
- Please contact us to book your consultation.